Introduction to Sensors
Table of contents
Control Systems
A control system manages and regulates a system to achieve desired outputs.
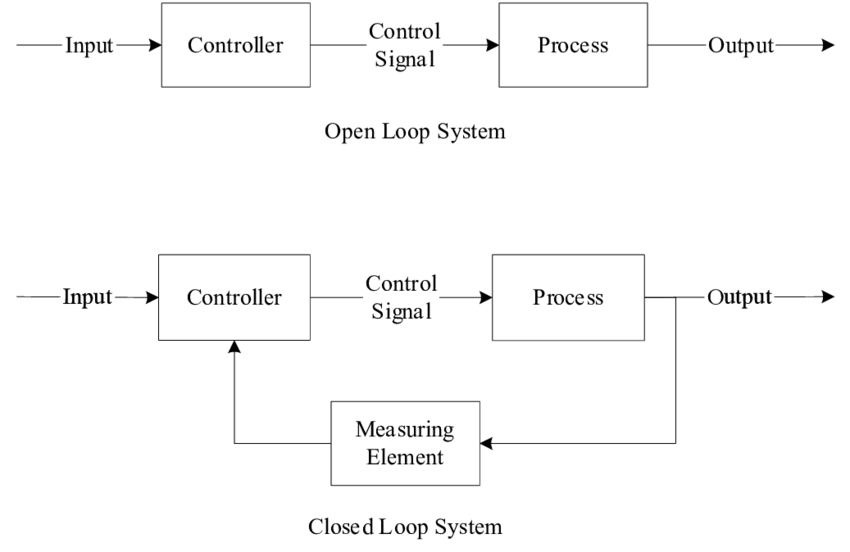
Open-Loop — Sends commands without feedback. It performs actions as directed but doesn’t adjust for errors or changes. Closed-Loop — Uses feedback to monitor outputs and adjust for accuracy.
Sensors
A sensor is a device that measures specific aspects of a machine’s environment and provides an output signal based on the detected data.
Sensors…
- Gather data about the robot and its environment
- Provide output signals that serve as inputs to the system
- Play a key role in closed-loop systems (gives feedback)
Types of Sensors
Rangefinder Sensors — Sensors that detect objects by emitting waves (such as sound or light) and measuring the time it takes for the waves to reflect off an object and return to the sensor. These sensors can use various types of waves, such as ultrasonic in the XRP Minibot.
-
Applications
Obstacle avoidance, Distance measurement, Collision detection
Reflective Sensors — Sensors that detect objects by emitting various types of light, such as infrared in the XRP Minibot, and measuring the amount of light reflected back.
-
Applications
Line-following, Positioning